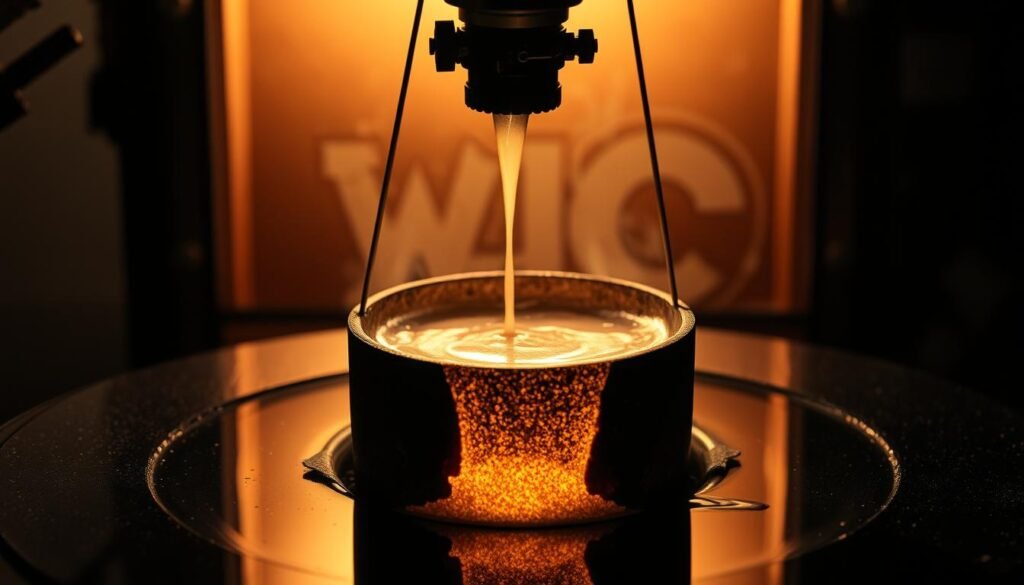
The melting of Lead is important in many fields. It is very useful because of its low melting point.
In the lead melting process you work at low temperatures. This is very advantageous in the metalworking industry. Despite health risks, Lead it is indispensable in some areas.
To safely melt lead, you need the right technique and safety measures. This article is for hobby metalworkers and experts. You will learn more here about melting lead.
Melting point of lead
The melting point of lead is 327 °C. This is relatively low compared to metals like iron or copper.
This makes lead ideal for DIY enthusiasts. You don't need large, expensive furnaces.
It is important to find the right temperature for melting lead. This prevents the metal from becoming too hot.
This allows for more precise shapes and saves energy. That's good for the environment and reduces costs.
327 °C: Low-temperature advantages
The melting temperature of 327 °C offers many benefits. Some of them are:
- Lower energy consumption when melting
- More precise shaping through controlled temperature
- Reduced tool wear due to lower temperatures
- More environmentally friendly processing through lower energy use

Lead is very popular because of these advantages. It is used in batteries and for radiation shielding. By understanding the thermal properties of lead, manufacturers and DIY enthusiasts can improve their products. This can help reduce costs and environmental impact.
Safety Aspects
Caution is advised when melting lead to prevent health damage. Lead is a toxic heavy metal. Improper handling can cause serious health problems.
Health Risks
Lead fumes produced during heating are very dangerous. They can be easily inhaled. Lead poisoning can damage the nervous system and blood formation.
Long-term Lead Exposure can lead to chronic health problems. These include neurological damage and anemia.
Lead fumes can also cause headaches, fatigue, and concentration problems. It is important to be aware of the risks and take precautions.
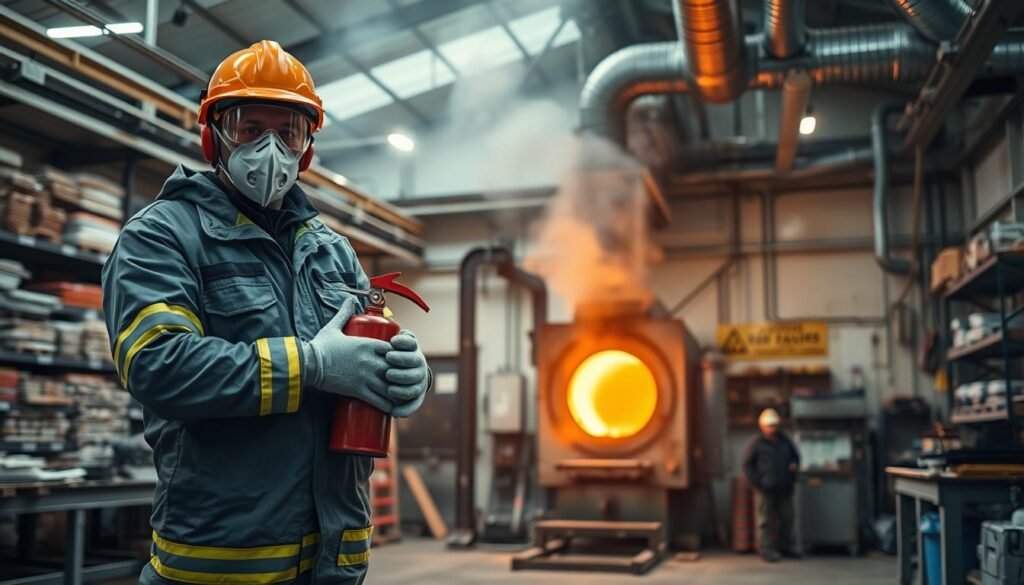

Protective Measures
To minimize risks when melting lead, protective measures are important. Wear Respiratory masks with special filters, heat-resistant gloves and protective clothing.
A well-ventilated workspace is also important. Melting lead should be done outdoors or in well-ventilated rooms. Avoid working near food or children.
- Use appropriate protective clothing and equipment.
- Ensure adequate ventilation in the workplace.
- Avoid melting lead near food or children.
Application areas
Molten lead is used in many areas, especially in radiation shielding and batteries. Its unique properties make it indispensable.
Radiation shielding
Lead provides good protection against X-ray and gamma radiation. It is used for radiation shielding walls and panels. You can find these in hospitals, nuclear power plants, and research laboratories.
At low temperatures, lead can be processed precisely. This results in custom protective measures. This is very important where radiation protection matters.
Batteries
Lead is also found in lead-acid batteries. These are popular in many vehicles and for power supplies. The manufacturing process of lead plates and grids is complex.
The use of lead in batteries demonstrates its versatility. It is also used in fishing weights, solder for plumbing, and in lead casting for divination purposes.
The future of lead in industry looks promising. Research and development are constantly seeking new applications and improvements.
Processing strategies
To work with molten lead, special methods are required. This ensures precision and quality. Lead is soft, making it easy to work with. This makes it perfect for fine casting work.
Precision casting using suitable molds
Silicone, sand, or metal molds are often used for precision casting. These molds help shape lead accurately. They are ideal for complex parts.
Tool selection for lead processing
Choosing the right tool is very important. Special crucibles, heating sources, and temperature measuring devices are needed. These help control the temperature precisely.
Special cutting tools, files, and grinding materials are needed for post-processing. These are calibrated to the softness of lead. With the right tools and techniques, lead can be processed efficiently. This results in great outcomes.